14. The Stream API
The Stream API
In this section, you will learn to:
- Compare "functional programming" and "imperative programming" styles
- Define what a Java Stream is and what it does
- Identify common intermediate and terminal stream operations
ND079 JPND C2 L01 A11 The Stream API V3
What is a Stream?
A stream is a sequence of elements.
Streams are useful because they allow us to process collection, one element at a time. They can process elements in many ways, such as (but not limited to) filtering or transforming elements, sorting elements, or computing statistics such as the sum or average.
Stream Pipelines
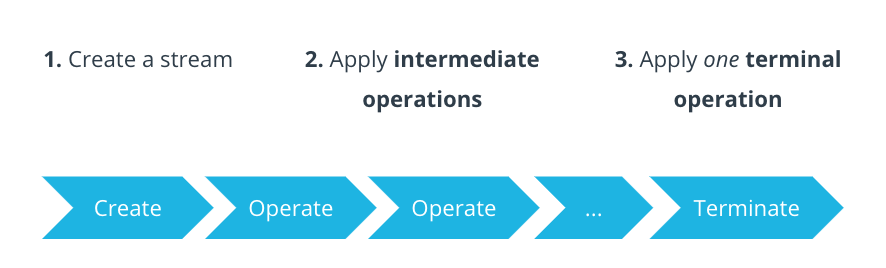
You Can Apply Many Intermediate Operations, But Only One Terminal Operation, To a Stream
A stream pipeline consists of creating a stream, calling intermediate operations on the stream, and then terminating the stream using a terminal operation.
Streams are single-use. Once you do an operation on a
Stream, you cannot to any more operations on that same stream. This means intermediate operations always return a brand newStream, never the original.Streams are lazily evaluated. No computation happens until the very end, when the terminal operation is called.
Example
void printScores(List<Student> students) {
return students.stream()
.filter(Objects::nonNull)
.mapToInt(Student::getScore)
.forEach(System.out::println);
}First, the stream() method creates a stream from the students list.
This stream pipeline has two intermediate methods: the filter() method removes the elements of the stream that are null, and mapToInt() transforms each student into an int. Notice that each of these methods returns another Stream: filter() returns a Stream<Student>, and mapToInt() returns an IntStream.
Finally, the terminal operation max() computes the maximum value in the IntStream. This terminal method actually returns an OptionalInt instead of an int. If the students parameter is empty or contains only null elements, it's possible the final stream will be empty. In this case, we need to tell the program to return a default value of 0.
QUIZ QUESTION::
What is the correct order of a Stream Pipeline?
ANSWER CHOICES:
|
Order |
Operations |
|---|---|
1 |
|
2 |
|
3 |
SOLUTION:
|
Order |
Operations |
|---|---|
|
1 |
|
|
3 |
|
|
2 |